Archaic

The
Archaic Era is marked by the steady building and development of
the inhabitants of the Aegean lands and the Athenian rise to prominence.
The most enduring artistic endeavors of this
era would be the development and perfection of what has come to
be known as Black-Figure, followed by Red-Figure Vase production.
Vase painting was the major pictorial art of the Greeks. Although
vases performed a practical service they embodied the best the society
had to offer in craftsmanship and decoration.
 |
 |

Attic Black-Figure
Erotic Bank Cup C.
540 - 530 B.C..
|
 |
East
Greek Painted Terracotta Female Head C.
7th Century B.
|
 |
Attic
White-Ground Lekythos
Early 5th Century B.C
|
 |
Attic
Small Red-Figure Mug
Late 5th Century B.C.
SOLD |
 |
Attic
Red-Figure Trefoil Oinochoe Figured Vase
490-480 B.C.
SOLD
|
|

Classical 480-330 B.C.
Many advances
were made in the portrayal of detail, musculature and body orientation
by the artists of the late Archaic Period. The most astounding
accomplishment was the achievement of two-dimensional naturalism
for the first time in history. This set the stage for what is
referred to as Classical Greece.
This period,
beginning with the defeat of the Persian invaders, coincided with
advances in the technique of Greek artists that demonstrated a full
realization of the human body. There was a confidence apparent in
the art of this period which came to a close with the ascendancy
of Alexander the Great.
 |
 |
Greek
Terracotta Protome
Veiled Female Bust
Magna Graecia 460-450 B.C.
SOLD |
 |
Greek
Terracotta Aphrodite,
from Canosa
3rd Century B.C.
|
 |
Greek
Terracotta
Aphrodite Figure
3rd Century B.C
|
|

Hellenistic 336-146 B.C.
Hellenistic art
refers to Grecian art produced during the period that began when
Alexander the Great became King of Macedonia and represents the
final chapter of ancient Greece. Hellenistic style was elegant and
strove to express emotion and emphasize the dramatic. The Greek
Empire expanded far beyond its previous boundaries and held much
influence throughout its lands. Also during this era, Greek colonies
that had been established in Southern Italy were beginning to gain
artistic recognition. With the death of Alexander the Great and
the absence of a strong predecessor, the Greek civilization was
torn apart by rivalries and declined until it eventually succumbed
to Roman rule
 |
 |
Gold
Olive Leaves (12)
3rd Century B.C.
SOLD
|

Apulian 400-320 B.C.
Apulia,
referring to an area of Southern Italy, had been settled by the
Greeks during the Archaic period. But it was during the late Classical
and Hellenistic Era that Apulia began to come into its own and compete
directly with Athens in the production of pottery. It is believed
that the Peloponnesian War caused many Athenian potters and artists
to relocate to Apulia, and the fine quality of decorated pottery
from that region gained prominence. By the close of the Hellenistic
period, vase production in Athens had all but ended.

|
 |
Apulian
Red-Figure Owl Skyphos
400 B.C.
|
 |
Apulian
Gnathia Epichysis
C.330-320 B.C.
SOLD
|
 |
Apulian
Chalcidizing Cup
400-320 B.C.
SOLD
|
 |
Apulian
Red-Figure Bell Krater
C.340 B.C.
SOLD
|
 |
Apulian
Red-Figure Trefoil Oinochoe
C.350-325 B.C.
SOLD
|

Etruscan
The Etruscan
civilization arose in the land of Etruria,
a region of Italy. It comprised 12 loosely bound citi-states that
shared a common language and religion. The Greeks had first made
contact with the Etruscan people around 800 B.C. and they were gradually
drawn into mainstream Mediterranean culture. The Etruscans never
really developed an artistic style of their own but adopted the
Greek ideal and executed it with their own individualistic, colorful
flair. The artifacts are evidence that they were very gifted craftsmen.
Eventually their culture became completely absorbed by the rising
power of Rome and by the first century B.C. had ceased to exist.

|
 |
Etruscan
Polychrome Terracotta Antefix Cerveteri, Etruria
C.500 B.C
SOLD
|

Cypriot
Cypress, an island in the Mediterranean, was Greek during this period.
According to Greek Mythology it was the birthplace of Aphrodite
and was an important and esteemed land.

|
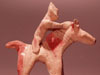 |
Cypriot
Bi-chrome Ware Terracotta Horse and Rider
700-600 B.C.
 |
 |